Editor’s note: As what we know about COVID-19 evolves, so could the information in this story. Find our most recent COVID-19 articles here and learn the latest in COVID-19 prevention at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Some photos and videos on this site were filmed prior to the COVID-19 outbreak or may not reflect current physical distancing and/or masking guidelines.
Understanding changing guidelines and the differences between COVID-19 test types can be confusing, especially when you’re deciding when it’s best to get back to work or socializing after a COVID-19 infection.
Here’s what to know about infectiousness, quarantines and testing once you’ve tested positive for COVID-19:
How do I know if I’m still contagious from my COVID-19 infection?
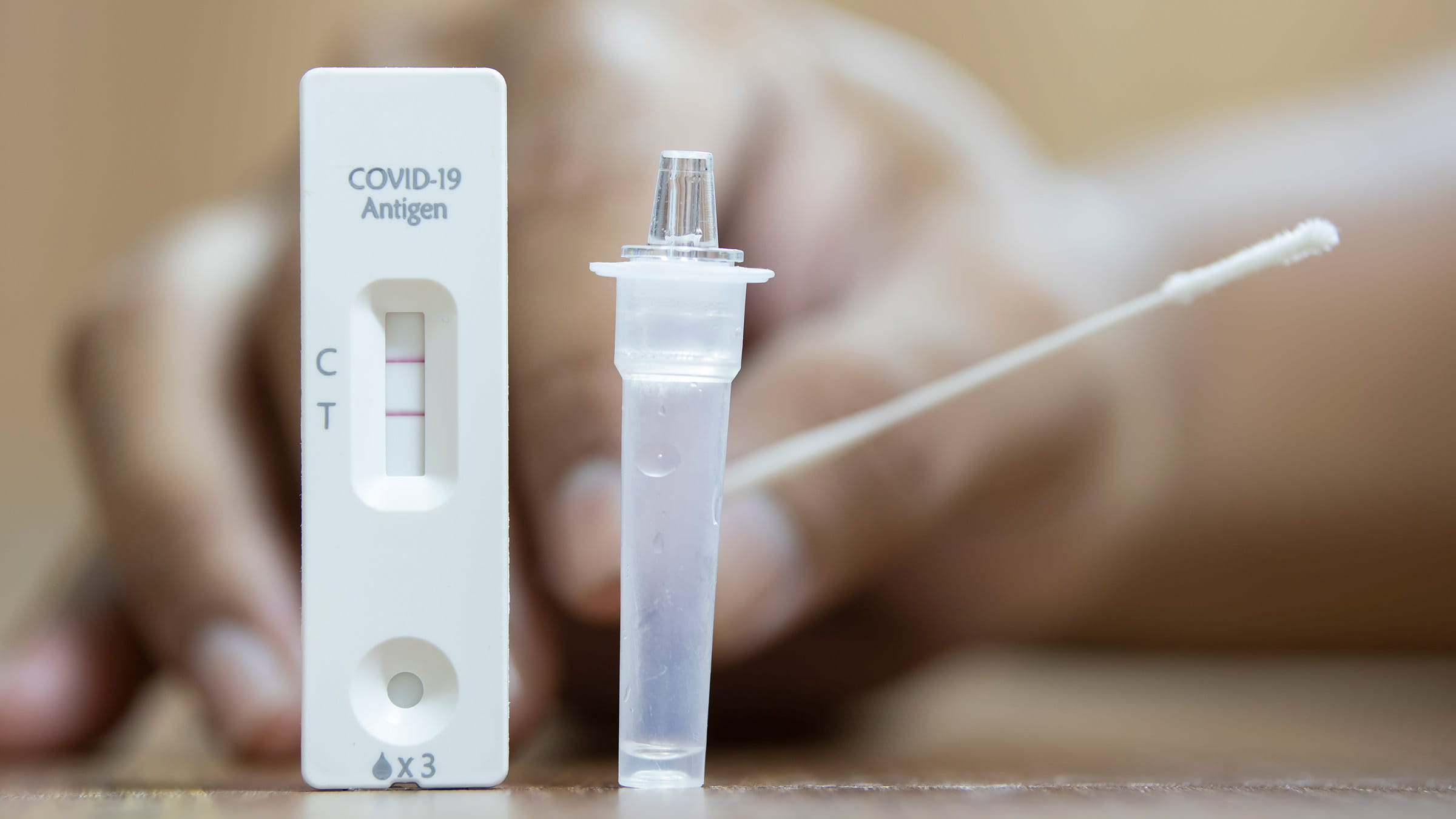
It’s best to follow CDC guidelines for quarantine and isolation. They have a very helpful and user-friendly interactive calculator online. To ensure that you’re no longer contagious after the CDC’s recommended isolation period for you, you can take an antigen test (often referred to as a rapid test). If it’s negative, you’re likely no longer contagious.
I’ve heard that I can continue to test positive for COVID-19 for months, even when I’m not contagious. Should I disregard any positive test results after a certain number of days?
If you’ve followed CDC guidelines for isolation after infection and you’re outside of your isolation period, you might still test positive on a PCR test for up to 90 days after a COVID-19 infection without being contagious. However, home rapid tests (antigen tests) don’t work by the same mechanism and are still a good gauge of infectiousness.
If you get a positive test result from a PCR COVID-19 test within that 90-day window and it’s…
- preceded by a negative PCR test result in that same window AND
- coincides with COVID-19 symptoms
…then you should presume that you have an active COVID-19 infection/reinfection and are potentially contagious to others.
If you test positive on an antigen test within that 90-day window, you should also presume that you have a COVID-19 infection and could be contagious to others.
Have more questions about COVID-19 tests, such as how accurate rapid tests are, how they compare to lab or doctor’s office tests and when to use a rapid test vs. a PCR test?

Ready to get vaccinated?
We have appointments available as early as today.
Schedule now




